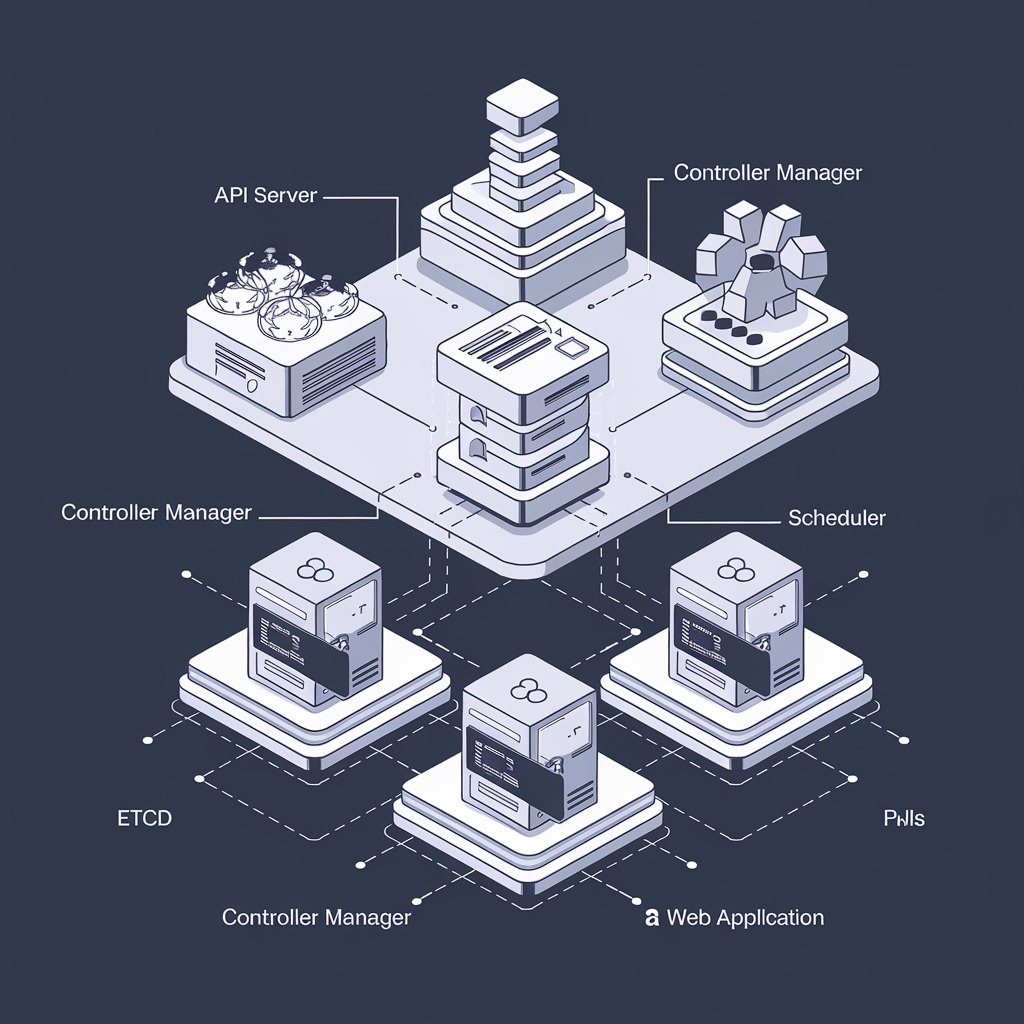
Kubernetes is a powerful orchestration tool for managing containerized applications. One of the essential features it provides is the Deployment resource, which simplifies the process of deploying and managing applications at scale. Let’s dive into what Kubernetes deployments are and how they can help you streamline your application lifecycle.
What is a Kubernetes Deployment?
A Kubernetes Deployment is a resource that provides declarative updates to applications. It manages the deployment and scaling of a set of Pods, which are the smallest deployable units in Kubernetes. A Deployment ensures that the specified number of Pods is running at all times and can be updated, scaled, or rolled back seamlessly.
Key Features of Deployments
- Declarative Configuration: You define your desired state in a YAML file, and Kubernetes takes care of the rest, ensuring that your application runs as specified.
- Rolling Updates: Deployments allow you to update your application with zero downtime. Kubernetes gradually replaces old Pods with new ones, ensuring that some Pods are always available to serve traffic.
- Rollbacks: If an update goes wrong, Kubernetes makes it easy to revert to a previous version of your application, minimizing disruption.
- Scaling: You can easily scale your application up or down by adjusting the number of replicas in your Deployment configuration.
- Self-healing: Kubernetes automatically restarts failed Pods, replaces them, and reschedules them as necessary, ensuring that your application remains healthy.
Creating a Kubernetes Deployment
To create a Deployment, you need to define a YAML file that specifies the desired state of your application. Here’s a simple example for a Nginx deployment:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.19
ports:
- containerPort: 80
In this example:
- replicas: Specifies that we want three instances of the Nginx Pod running.
- selector: Defines how the Deployment finds which Pods to manage.
- template: Describes the Pods that will be created, including the container image and ports.
kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
Kubernetes will then create the specified number of Pods, ensuring they are running and ready to serve traffic.
Managing Your Deployment
You can easily manage your Deployment using several kubectl commands:
- Check the status:
kubectl get deployments
- Update the Deployment: Modify your YAML file and apply the changes again. Kubernetes will perform a rolling update automatically.
- Rollback to a previous version:
kubectl rollout undo deployment/nginx-deployment
Conclusion
Kubernetes Deployments are a fundamental component of managing applications in a Kubernetes cluster. They provide powerful features for rolling updates, scaling, and ensuring the availability of your applications. By leveraging Deployments, you can streamline your application lifecycle management, enhance reliability, and maintain continuous delivery practices.